Tired of constantly replacing rechargeable batteries for your Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV), two-wheeler power batteries, or portable energy storage devices? Wondering why some lithium rechargeable batteries fail after just one year while others maintain stable performance for a decade? The answer is simple: not all rechargeable batteries are created equal. By mastering battery chemistry principles and maintenance techniques, you can select and care for durable rechargeable batteries to achieve long-term stable power supply. Below is a detailed guide on how to choose and maintain rechargeable batteries for more reliable power.
Why Most Rechargeable Batteries Fail Too Soon
For most users, rechargeable batteries are both a convenience and a frequent hassle. Research shows that the average user replaces rechargeable batteries 4-6 times a year, wasting money and generating unnecessary waste. But this vicious cycle can be broken. The lifespan of rechargeable batteries depends primarily on two core factors: their chemical composition and how they are used and maintained.
Among all rechargeable batteries, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries stand out. With proper maintenance, these high-cycle rechargeable batteries can last 5-10 years and withstand 2,500-9,000 charge-discharge cycles—far exceeding NMC or nickel-based rechargeable batteries. However, even the highest-quality rechargeable batteries will underperform if critical details like charging habits, temperature exposure, and storage conditions are ignored. Below is a breakdown of key steps to prevent premature battery failure.

Rechargeable Battery Comparison: Which Has the Longest Lifespan?
Battery Type | Typical Lifespan | Cycle Count Before Capacity Degradation | Core Advantages | Applicable Scenarios |
LFP | 5-10 Years | 2,500-8,000 Cycles | Excellent Durability, High Safety, High Temperature Resistance | Portable Energy Storage, Two-Wheeler Power Batteries, AGVs, Heavy-Duty Truck Starter Batteries |
NMC | 2-3 Years | 500-1,500 Cycles | High Energy Density, Lightweight, Compact | Portable Energy Storage Auxiliary Power, Small Portable Devices |
NiMH | 1-2 Years | 500-1,000 Cycles | Cost-Effective, Easily Accessible, Environmentally Friendly | AGV Low-Power Accessories, Small Portable Energy Storage |
Lead-Acid | 3-5 Years | 300-500 Cycles | Low Cost, Stable Power Supply, Easy to Recycle | Traditional Fuel Vehicle Starters, Low-Cost Low-End Backup Power |
1. LFP: The Longevity Champion
If you need long-lasting rechargeable batteries, LFP is the top choice. Designed for heavy-duty applications, these rechargeable batteries have a stable chemical structure that resists degradation even with frequent charging—making them ideal for portable energy storage, two-wheeler power batteries, and AGVs. Although their energy density is lower than NMC batteries (i.e., less energy storage per unit weight), their excellent temperature resistance and thermal runaway prevention capabilities make them the safest and most reliable option for long-term use.
2. NMC: The Portable Power Pioneer
NMC rechargeable batteries excel in applications like portable energy storage auxiliary power and small portable devices. Their high energy density enables long-lasting power for small equipment, and their lightweight, compact design makes them perfect for portable devices. However, these batteries are sensitive to environmental conditions: exposure to temperatures above 35°C or frequent deep discharge to 0% can halve their lifespan. With proper care, though, they can easily exceed their expected 2-3 year lifespan.
3. NiMH: The Cost-Effective Option
NiMH rechargeable batteries are ideal for non-continuous power devices such as AGV low-power accessories and small portable energy storage. They are more affordable than lithium-based batteries and widely available. Their main drawback is high self-discharge—they lose power even when not in use, which can lead to depletion after long-term storage. Regular full charging and frequent use can effectively mitigate this issue.
4. Lead-Acid: The Basic Application Workhorse
Lead-acid rechargeable batteries have a century-long history of application and are currently mainly used in scenarios like traditional fuel vehicle starters and low-cost low-end backup power. They are extremely affordable and provide stable power for low-power equipment. However, they have obvious drawbacks: bulky size, regular maintenance requirements (such as checking electrolyte levels), and limited cycle counts. These batteries are more suitable for basic scenarios where cost is a top priority and lifespan and performance requirements are low.
4 Practical Tips to Extend Rechargeable Battery Lifespan
Even the highest-quality rechargeable batteries cannot perform at their best without proper care. Master the following simple tips to significantly extend battery lifespan:
1. Charge Smart, Avoid Full Charges
The most common mistake users make with rechargeable batteries is charging them to 100% every time. For lithium-based rechargeable batteries like LFP and NMC, maintaining a charge level between 20%-80% can effectively reduce internal component wear. It is recommended to use an intelligent charger that shuts off at 80% and avoid leaving devices plugged in overnight. Lead-acid and NiMH rechargeable batteries, however, require full charging—frequent partial charging can cause “memory effect,” which reduces battery capacity.
2. Control Temperature, Avoid Extreme Conditions
Rechargeable batteries have a narrow optimal operating temperature range: 15°C-35°C (59°F-95°F). High temperatures accelerate chemical decomposition—storing batteries in high-temperature environments in summer can reduce their lifespan by 30% in a single season. Low temperatures, on the other hand, can cause lithium plating in lithium-based batteries, resulting in permanent capacity loss. Therefore, batteries should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated place away from direct sunlight.
3. Store Scientifically to Reduce Wear
If you need to store rechargeable batteries for equipment like AGVs and portable energy storage for an extended period (such as seasonal idleness), proper storage methods are essential to prevent damage. Lithium-based batteries should be stored at 50% charge to balance chemical activity and prevent over-discharge. Lead-acid rechargeable batteries need to maintain a 70% charge to avoid sulfation (a buildup of deposits on electrodes that hinders conductivity). Regardless of the battery type, they should be stored in a dry, cool place, avoiding environments with drastic temperature fluctuations like garages and attics.
4. Perform Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Routine maintenance is crucial for extending lifespan. It is recommended to check the condition of rechargeable batteries monthly for signs of swelling, leakage, or terminal corrosion. Wipe terminals with a dry cloth to remove dust and prevent poor contact, which can reduce performance and waste power. Lead-acid rechargeable batteries require regular topping up with distilled water (tap water is not allowed) to maintain electrolyte levels. Damaged batteries should be replaced immediately to avoid fire hazards.
Choose the Right Rechargeable Battery for Your Needs
The best rechargeable battery depends on your specific application. Below is a quick selection guide:
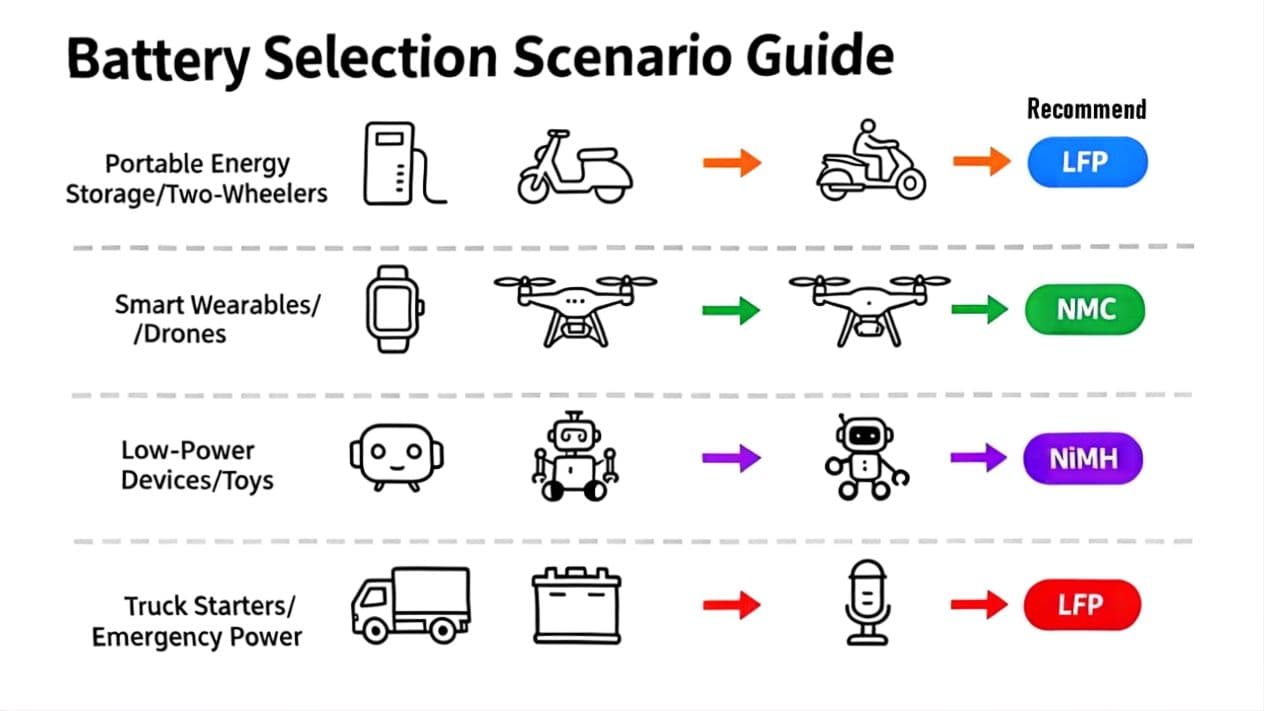
- Portable Energy Storage, Two-Wheeler Power Batteries, AGVs, Electric Forklifts: LFP Rechargeable Batteries (Longest lifespan, high safety, suitable for heavy-duty and high-frequency use scenarios)
- Smart Wearables, Small Drones, Portable Energy Storage Auxiliary Power: NMC Rechargeable Batteries (High energy density, lightweight, suitable for portable low-power devices)
- AGV Low-Power Accessories, Small Portable Energy Storage, Children’s Toys, Regular Remotes: NiMH Rechargeable Batteries (Cost-effective, easy to purchase and replace, suitable for low-power non-continuous use scenarios)
- Heavy-Duty Truck Starter Batteries, Outdoor Emergency Power, Home Backup Power: LFP Rechargeable Batteries (Strong durability, stable power supply, resistant to harsh environments and instantaneous high-power demands)
By choosing the right rechargeable battery and following maintenance tips, you can reduce replacement frequency, save costs, and minimize waste. Whether powering portable energy storage devices, two-wheelers, AGVs, or heavy-duty truck starter systems, selecting the right product and using it correctly ensures long-term stable power supply.



